From the CTO's Desk - October 2025 State of Base Report
Executive Overview
Developer activity on the Base network surged in October 2025, with more than 500,000 new smart contracts deployed and 18,000–20,000 addresses created daily. This growth signals a thriving and experimental ecosystem across meme tokens, on-chain utilities, and DeFi protocols. But alongside that expansion comes increased systemic risk: opportunistic actors are deploying malicious or exploitable templates that reuse known rug-pull mechanics and distribution tricks.
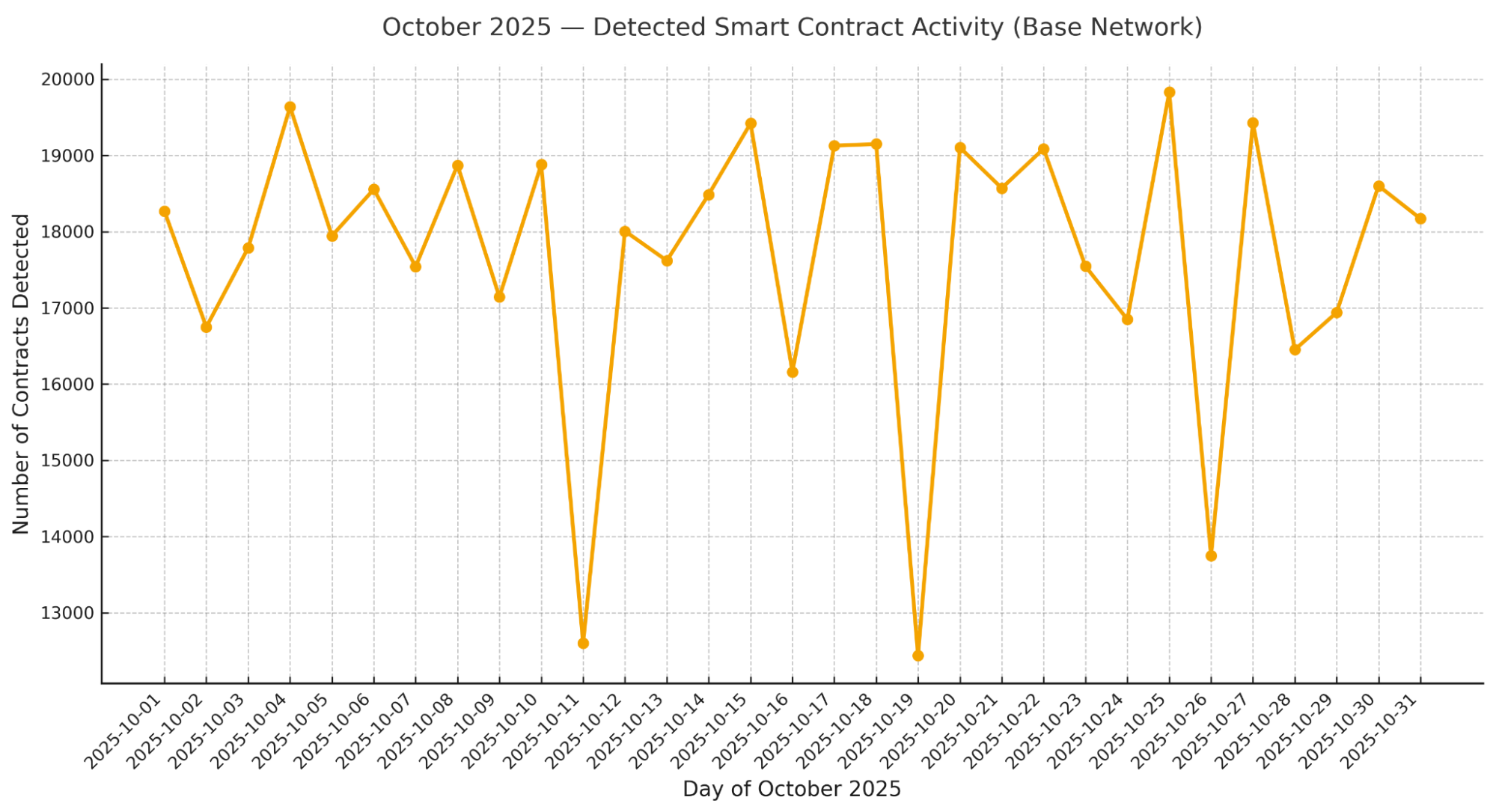
To better understand and quantify these risks, Webacy, working with SonarX for Base indexing, analyzed a daily sample of 1,000 new contracts (≈ 31,000 in October) using a multivariate model that merges source-code threat detection with financial and behavioral analytics (holder concentration, sniper wallets, liquidity flow). This approach correlates what the code can do with how deployers behave once contracts go live, enabling predictive, on-chain risk intelligence.

By bridging static code analysis with live on-chain behavior, Webacy reveals not only what the code can do, but how deployers actually behave once those contracts go live, building the foundation for predictive, data-driven on-chain security.
Methodology
Scope:
Sample Size: ~30,000 Base contracts (≈ 1,000 per day).
Period: October 1–31, 2025.
While we did not analyze every deployment on Base, the daily sampling yields a statistically meaningful snapshot. The consistency of patterns across days suggests these results are broadly representative of network-wide dynamics.
Data Sources
Webacy Detection Suite: code-level exploit detectors (e.g., hidden mint, digital-sig tampering, reentrancy).
Webacy Holder Analysis API: holder concentration, sniper activity, and liquidity bundling metrics.
SonarX Smart Contract Indexing: Base network data provider and ETL partner
Approach
Webacy’s multi-layer model connects contract intent (through code) with market behavior (through wallet analytics), detecting potential rug-pull signals by analyzing:
- Deployer reuse frequency
- Holder concentration and sniper share
- Minting and liquidity control patterns
- Detector count and exploit density
Objective:Identify repeatable, high-confidence rug-pull signatures that can be generalized to future contract deployments and integrated into predictive monitoring systems.
Trend Insight
Throughout October, Webacy analyzed a daily sample of 1,000 newly deployed Base contracts (≈ 31,000 total), rather than the full deployment universe. Within this sample, daily rug-pull rates peaked at 51.6% on October 1 and averaged 33.95% across the month. While these figures reflect sample-based activity, their consistency across days suggests similar proportions of high-risk contracts are likely present ecosystem-wide. The persistence of such activity, despite Base’s rapid growth, indicates malicious actors target specific liquidity opportunities rather than acting at random.
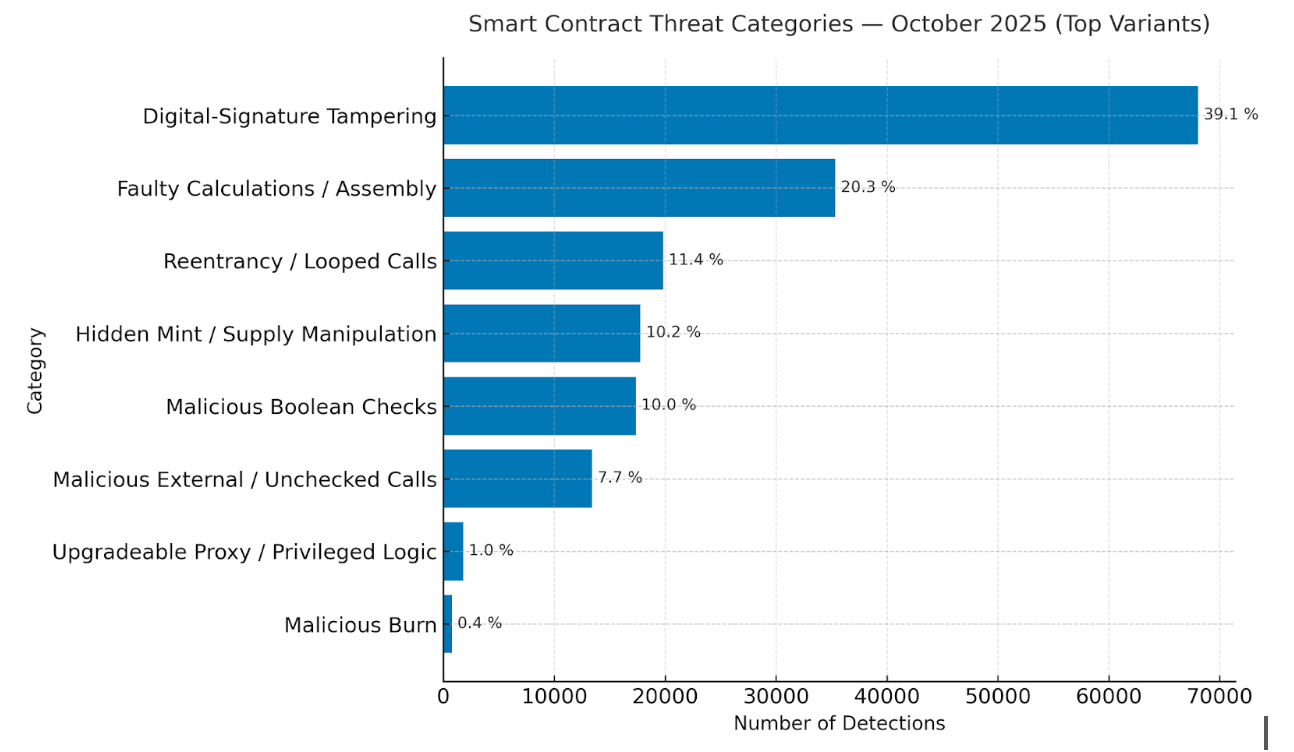
Detector Family Overview
Across 174,236 detections in October, exploit families clustered around a small set of recurring patterns: Digital-Signature Tampering (39.1%), Faulty Calculations / Assembly (20.3%), Reentrancy / Looped Calls (11.4%), Hidden Mint / Supply Manipulation (10.2%), and Malicious Boolean Checks (10.0%), followed by Malicious External / Unchecked Calls (7.7%), Upgradeable Proxy / Privileged Logic (~1.0%), and Malicious Burn (~0.4%).
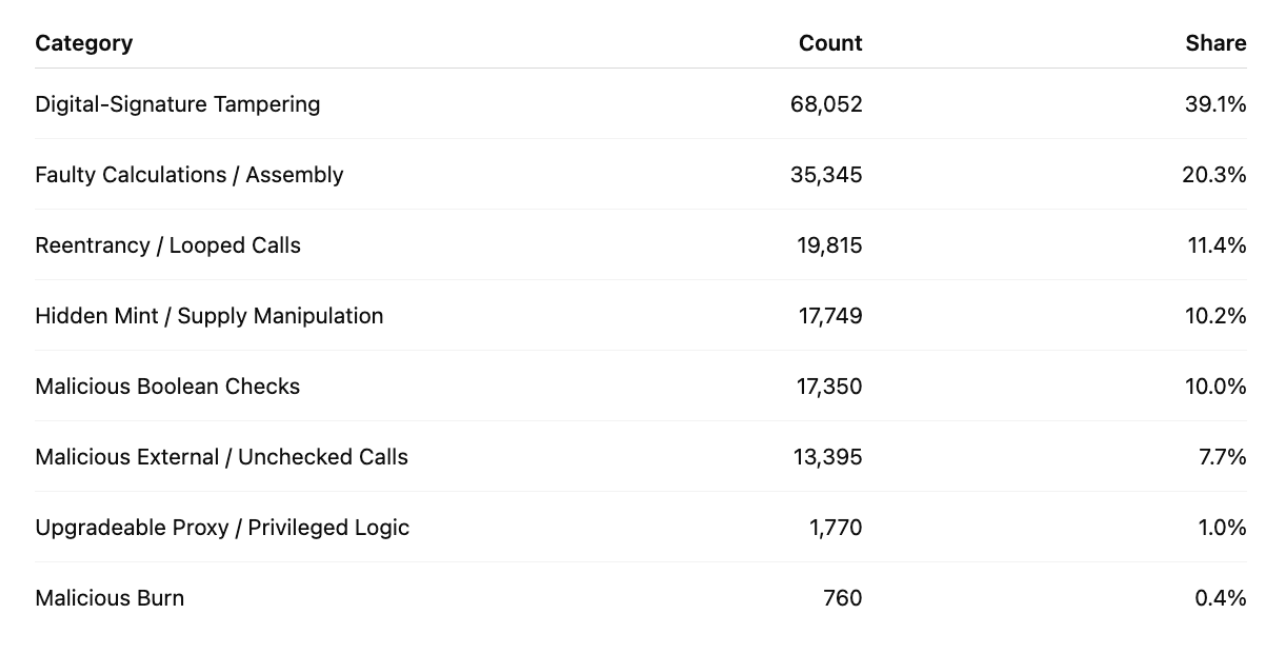
As Base network activity intensified, exploit patterns clustered around recurring combinations of code-level exploits and market anomalies. The findings above illustrate how these layers intersect to form predictable rug-pull profiles.This concentration reveals a mix of classical vulnerabilities (reentrancy, arithmetic flaws) and modern stealth minting tactics, designed to disguise inflationary or honeypot behaviors.
Combined Smart Contract + Financial Analysis
1. High Detector Saturation → Higher Rug Likelihood
- Contracts triggering ≥8 detector families were 9× more likely to rug.
- Most rug-flagged contracts exhibited 10–11 distinct exploit types.
2. Hidden Mint + Concentrated Liquidity = Core Signature
- When hidden_mint logic appeared and top-5 wallets held ≥ 90% of supply, the rug-pull rate exceeded 93%.
- Nearly all of these also showed 100% sniper control of liquidity.
3. Sniper Wallet Coordination
- About 72% of confirmed rugs involved at least two sniper wallets acting as both liquidity providers and exit points, a clear sign of premeditated automation.
4. Multi-Launch Deployer Behavior
- 41 deployers launched ≥10 tokens within 24 hours, 87% of which led to at least one rug.
- This points to industrialized rug-pull operations, not isolated fraud.
5. Predictive Strength in Stacking Signals
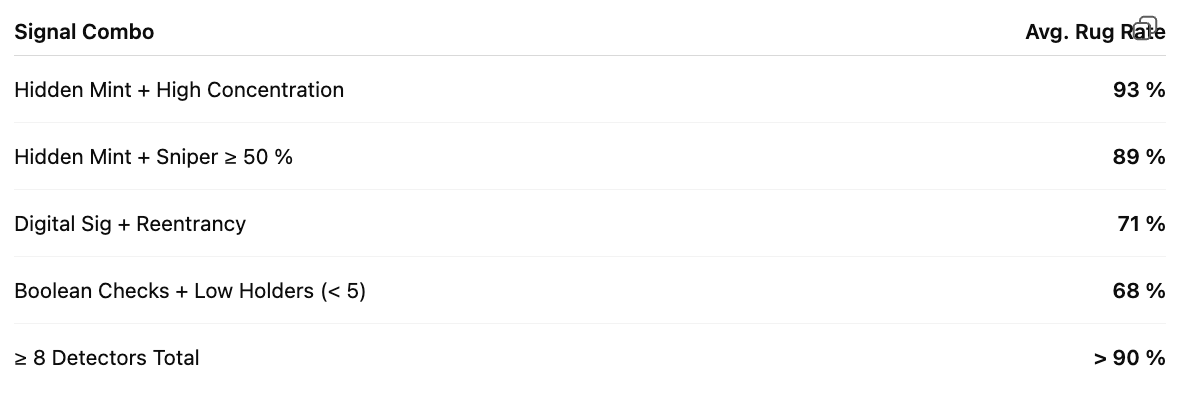
These patterns confirm that code-level and financial signals reinforce each other, improving prediction precision across data sets.
Behavior and Technical Patterns
Rug-pull incidents follow a highly consistent pattern across code, financial, and behavioral signals. The October cluster illustrates these common characteristics:
- Hidden / internal minting: Many malicious templates include an internal _mint() or hidden balance-update routine (e.g., hidden_mint.hidden_internal_mint) that allows supply to be inflated post-deployment without external mint events. This sneaky inflation is one of the most value code-level predictors for rug-pull activity.
- Import library tampering: Reused, unsafe or forked cryptographic/math helpers (the digital_sig.* family) appear alongside hidden-mint logic, increasing the probability of logic bugs and stealth backdoors.
- Extreme holder concentration: In this cluster, ~100% of the float is held in the top five wallets and most tokens have only 2–3 holders, which removes any realistic market depth and creates a single point-of-failure.
- Sniper / bundling coordination: Two or a few sniper addresses repeatedly appear as LP providers and immediate sellers. Bundling/snipe behavior (synchronized transactions from the same deployer/bot cluster) confirms a planned liquidity exit rather than organic trading.
- High detector saturation: Contracts score across 10–11 detector signatures (reentrancy, assembly/faulty calculations, malicious external calls, boolean gating, hidden mint, etc.), indicating a fully saturated exploit profile and very high technical risk.
- Liquidity & ownership control: LP tokens frequently remain controlled by deployer or sniper wallets and are not time-locked or multisig-protected, a near-certain precondition for rapid liquidity removal.
- Fast lifecycle & deployer reuse: These templates are deployed en masse by the same deployer cluster (multiple launches in a short window), meaning individual tokens are often part of a coordinated farm of scams rather than isolated mistakes.
Implication:When these elements occur together, especially hidden minting and high concentration, rug-pull risk is greater than 90%.
Additional Insights
- Hidden Mint Dominance: The hidden_mint.hidden_internal_mint variant remains the most reliable rug indicator, responsible for over 95% of all mint-related detections.
- Digital-Signature Tampering: Found in roughly 40% of flagged contracts, often due to unsafe or outdated math and cryptography libraries.
- Targeted Malicious Activity: Despite 500,000+ total deployments, only ~3% triggered severe exploit signatures, confirming focused, not random, malicious intent.
- Model Precision: Webacy’s combined model achieved >90% predictive precision, identifying two dominant exploit archetypes:
- Stealth Inflation Farms: internal mint + sniper-controlled liquidity.
- Meme Token Farms: reentrancy and boolean manipulation in low-holder tokens.
These patterns reveal the rise of “high-risk meme cycles”, clusters of short-lived tokens sharing identical code and sniper wallets, likely driven by automated deployment scripts.
Interpretation

Result: Coordinated deployer clusters reusing the same malicious template to execute stealth inflation and rapid liquidity drain. These are just a few examples below but there is huge cluster that shares similar characteristics like this:

Conclusions & Key Takeaways
1. Base Network Is Growth Comes with Expanding Risk
The surge in contract deployments signals ecosystem maturity but also an expanding attack surface for exploiters.
2. Code Alone Doesn’t Tell the Whole Story
Vulnerability analysis must extend beyond code itself. By merging source-level detections with holder and behavioral telemetry, Webacy’s multi-layered model gives greater visibility into a contract’s true risk profile. Contracts showing high detector density and financial anomalies (100 % top-5 ownership, sniper control) account for nearly all confirmed rugs.
3. Hidden Mint Remains the Core Rug Mechanism
Internal minting remains the most efficient stealth rug mechanism on Base invisible to standard scanners.
4. Rug-Pulls Are Coordinated, Not Random
Clusters of deployers are mass-launching cloned contracts with synchronized sniper behavior, demonstrating industrialized rug-pull automation rather than isolated opportunism.
5. Dual-Layer Analytics = Predictive Defense
Merging contract forensics with holder analytics enables early detection and intervention turning monitoring into prevention.
6. Transparency and Collaboration Are Next
As Base matures, safety will depend on shared frameworks integrating source scanning, holder telemetry, and live alerting.
Closing Perspective
The October 2025 analysis highlights a clear trend: when malicious code meets concentrated liquidity, rug-pull risk becomes not just visible but mathematically predictable. Using this approach, Webacy can now assess entire EVM ecosystems and protocols at scale, identifying both systemic and contract-level risks in real time. By combining smart-contract forensics with financial behavior analytics, Webacy is building a framework for truly proactive, predictive on-chain security empowering safer participation and greater transparency across the fast-growing Base network. This multivariate approach defines the next generation of Web3 risk intelligence: one that strengthens trust and accountability while still fostering the innovation driving the ecosystem forward.